import re
re regular expression
前提:处理的是字符串
效果:学习正则的语法规则,按照设定的规则,对字符串提取指定的内容--- 按照模块取字符串的指定内容
findall() 找到所有的符合条件的内容进行返回,返回的列表;如果没有找到,则返回空列表
re.findall(pattern=,string=,flags=) pattern正则表达式(即制定匹配规则) string要处理的字符串 flags
flags=re.I 忽略大小写
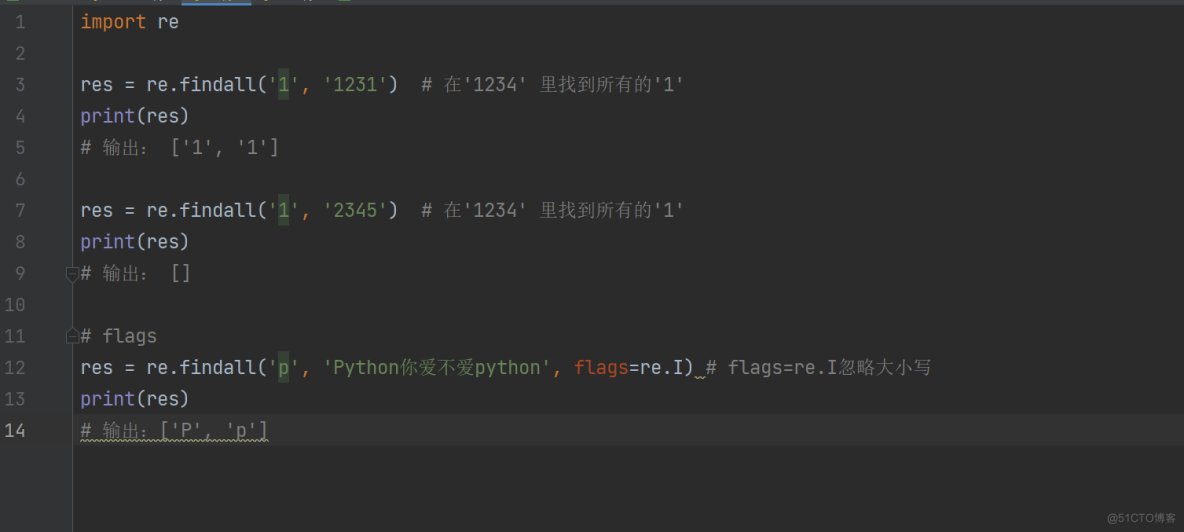
import re
res = re.findall('1', '1231') # 在'1234' 里找到所有的'1'
print(res)
输出: ['1', '1']
res = re.findall('1', '2345') # 在'1234' 里找到所有的'1'
print(res)
输出: []
# flags
res = re.findall('p', 'Python你爱不爱python', flags=re.I) # flags=re.I忽略大小写
print(res)
输出:['P', 'p']
import re
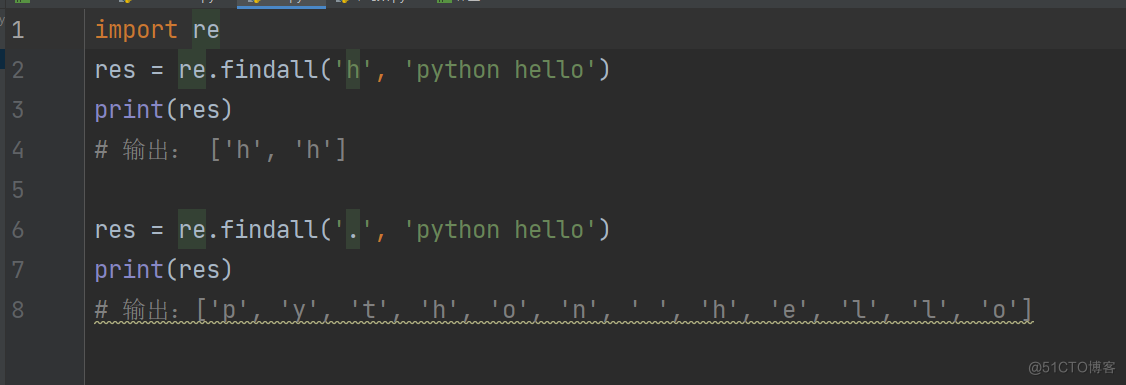
1. . : 匹配任意1个字符(除了\n)
import re
res = re.findall('h', 'python hello')
print(res)
输出: ['h', 'h']
res = re.findall('.', 'python hello')
print(res)
输出:['p', 'y', 't', 'h', 'o', 'n', ' ', 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']
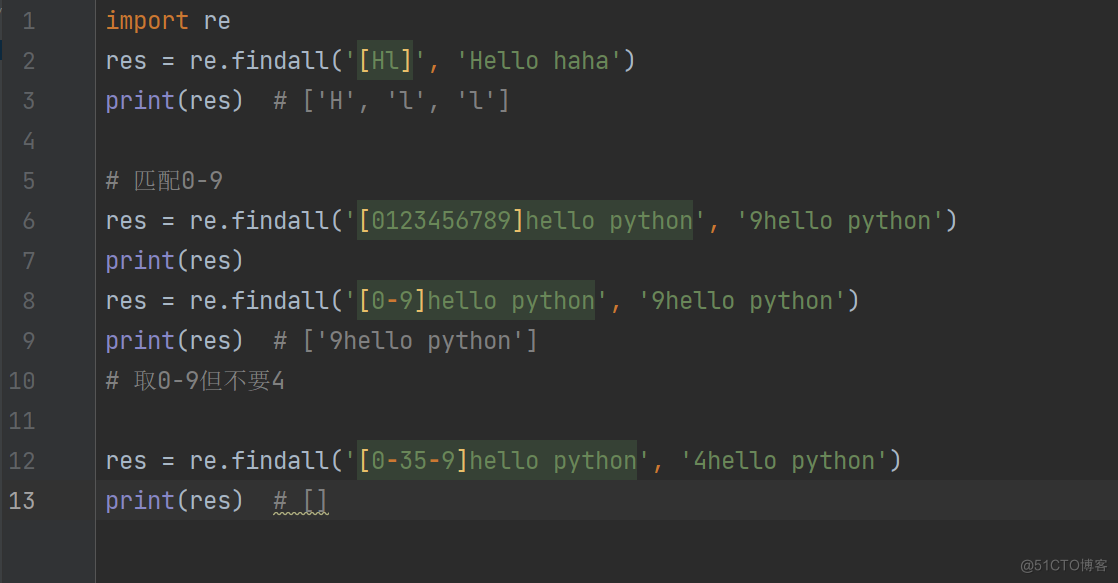
2.[]: 匹配[]中列举的一个字符
import re
res = re.findall('[Hl]', 'Hello haha')
print(res) # ['H', 'l', 'l']
# 匹配0-9
res = re.findall('[0123456789]hello python', '9hello python')
print(res)
res = re.findall('[0-9]hello python', '9hello python')
print(res) # ['9hello python']
# 取0-9但不要4
res = re.findall('[0-35-9]hello python', '4hello python')
print(res) # []
3. \d : 匹配数字,即0-9
import re
res = re.findall('今天是8号', '今天是8号吗')
print(res)
输出:['今天是8号']
res = re.findall('今天是8号', '今天难道是8号吗')
print(res)
输出:[]
res = re.findall(r'\d', '123')
print(res)
输出:['1', '2', '3']

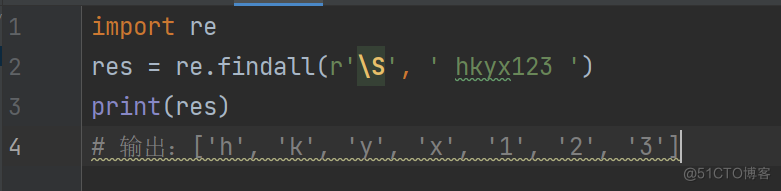
6. \S : 匹配非空白
import re res = re.findall(r'\S', ' hkyx123 ') print(res) 输出:['h', 'k', 'y', 'x', '1', '2', '3']
7. \w : 匹配单词字符,即a-z,A-Z,0-9,_ ,汉字
import re res = re.findall(r'\w','djksalgfdw3pt哈哈') print(res) 输出:['d', 'j', 'k', 's', 'a', 'l', 'g', 'f', 'd', 'w', '3', 'p', 't', '哈', '哈']

import re
import re
res = re.findall('[a-z][A-Z]*', 'hkyX12493') # 在符合条件的基础上,尽可能多地进行匹配
print(res)
import re
res = re.findall('[a-zA-Z]+python', 'Hellopython')
print(res) # ['Hellopython']
import re
res = re.findall('[1-9]?', '1234')
print(res) # ['1', '2', '3', '4', '']
import re
res = re.findall('[0-9]{6}', '12743294hgdkg')
print(res) # ['127432']
8-20的密码,可以是大小写、数字、字母、下划线
import re
res = re.findall('[a-zA-Z0-9_]{8,20}', 'DAJSDKL43240J哈哈GASDG_dklgf')
print(res)
import re
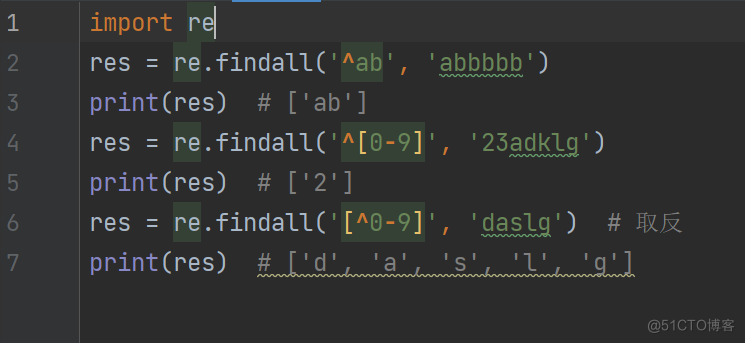
import re
res = re.findall('^ab', 'abbbbb')
print(res) # ['ab']
res = re.findall('^[0-9]', '23adklg')
print(res) # ['2']
res = re.findall('[^0-9]', 'daslg') # 取反
print(res) # ['d', 'a', 's', 'l', 'g']
总结:
'abc' 表示字符串有'abc'就匹配成功
'[abc]' 表示字符串中有'a'或'b'或'c'就匹配成功
'^abc' 表示的是以'abc'开头则匹配成功
'^[abc]' 表示字符串由'a'或'b'或'c'开头的
'[^abc]' 表示匹配'a' 'b' 'c'之外的字符
2. $ : 匹配字符串结尾
res = re.findall(r'\w*r$', 'hkyx') print(res) # [] res = re.findall(r'\w*r$', 'hkyxr') print(res) # ['hkyxr']
提取139邮箱
lst = ['haha@qq.com', 'hehe@139.com', 'jack@139.com']
for i in lst: # i为我们要处理的字符串
res = re.findall('.*@139.com$', i)
# print(res)
if res:
print(f'{i}符合条件')
else:
print(f'{i}不符合条件')

import re
1. |: 匹配左右任意一个表达式
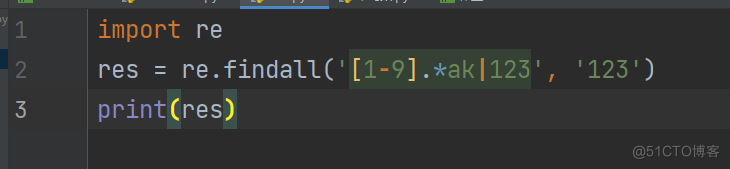
import re
res = re.findall('[1-9].*ak|123', '123')
print(res)
2.(ab): 将括号中字符作为一个分组
string = 'abcd1 abcd2 abcd3 abcd4'
1.不带括号
print(re.findall(r'\w+\s+\w+', string)) # ['abcd1 abcd2', 'abcd3 abcd4']
2.带括号---筛选---只返回括号里的内容
print(re.findall(r'(\w+)\s+\w+', string)) # ['abcd1', 'abcd3'] print(re.findall(r'\w+\s+(\w+)', string)) # ['abcd2', 'abcd4']
贪婪匹配:
在满足匹配时,匹配尽可能长的字符串,默认情况下,采用贪婪匹配.
非贪婪匹配:
在满足匹配时,匹配尽可能短的字符串,使用?来表示非贪婪匹配.
在量词 * ? + {m} {m,n}后直接加?,使贪婪变成非贪婪模式
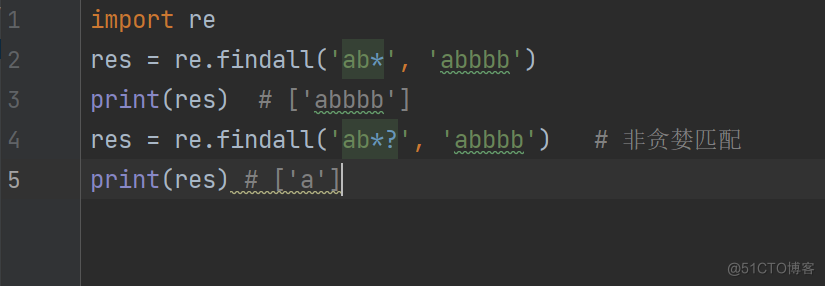
import re
res = re.findall('ab*', 'abbbb')
print(res) # ['abbbb']
res = re.findall('ab*?', 'abbbb') # 非贪婪匹配
print(res) # ['a']
如果觉得博客文章对您有帮助,异或土豪有钱任性,可以通过以下扫码向我捐助。也可以动动手指,帮我分享和传播。您的肯定,是我不懈努力的动力!感谢各位亲~
